Insulation materials play a vital role in modern engineering and technology, they can effectively reduce the speed of heat propagation, so as to achieve the role of heat preservation and energy saving in a variety of applications; to understand the working principle of the insulation materials, help us to better choose the type of insulation materials and develop more efficient construction methods.

Insulation materials work by reducing the efficiency of the three main modes of heat propagation - heat conduction, heat radiation and heat convection - through the use of low thermal conductivity materials with pore structures, etc., thus slowing down the transfer of heat.Below we first understand the three main modes of heat propagation:
1. Heat conduction
Heat conduction is the process of heat conduction from a high temperature object to a low temperature object, is essentially the object within the microscopic particles (such as atoms, molecules, etc.) thermal movement of the heat transfer phenomenon. The rate of heat conduction is significantly affected by the thermal conductivity of the material. For example, metals transfer heat quickly because of their high thermal conductivity. In contrast, insulating materials such as wood or plastic have a lower thermal conductivity and therefore slow down the transfer of heat.
Insulating materials usually have a low thermal conductivity, which makes the transfer of heat within them weaker. This is largely attributed to the molecular structure and compositional properties of the insulation material. For example, polymer materials and insulating silicate materials, for example, have a much lower thermal conductivity than high thermal conductivity materials such as metals. In addition, thermal insulation materials often contain air layers, such as fibre gaps in materials such as glass fibre and rock wool, as well as air bubbles in foam materials, which are structures that effectively slow down the rate of heat transfer.
2. Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation refers to the phenomenon that an object radiates electromagnetic waves due to its temperature, which widely exists in nature and man-made environment. For example, the radiation from the sun, the radiation from flames, and the infrared radiation from objects are all thermal radiation. All objects above absolute zero can produce thermal radiation, and the higher the temperature, the greater the total energy radiated.
Thermal insulation materials are often coated with highly reflective materials such as metals or special ceramics to reflect most of the thermal radiation, preventing it from entering the interior of the material, thus maintaining the stability of the internal temperature.
3. Thermal convection
Thermal convection refers to the fluid (liquid or gas) due to the macro-movement of the fluid (liquid or gas) so that the relative displacement between the parts of the fluid, hot and cold fluids mixed with each other and the heat transfer process. Thermal convection can be driven by the external role of forced convection, can also be caused by temperature differences in density changes caused by natural convection.
Insulation materials often have a porous structure that traps and stores large amounts of air, reducing the potential for thermal convection by reducing air movement. At the same time, some insulation materials are designed with a layered structure that effectively prevents convection from occurring by increasing the length of the heat transfer path.
In summary, the working principle of heat-insulating materials involves the delicate regulation of various heat transfer methods such as heat conduction, heat radiation and convection. By choosing the right materials and designing the structure, heat-insulating materials can effectively reduce heat transfer and protect the stability of the internal temperature.

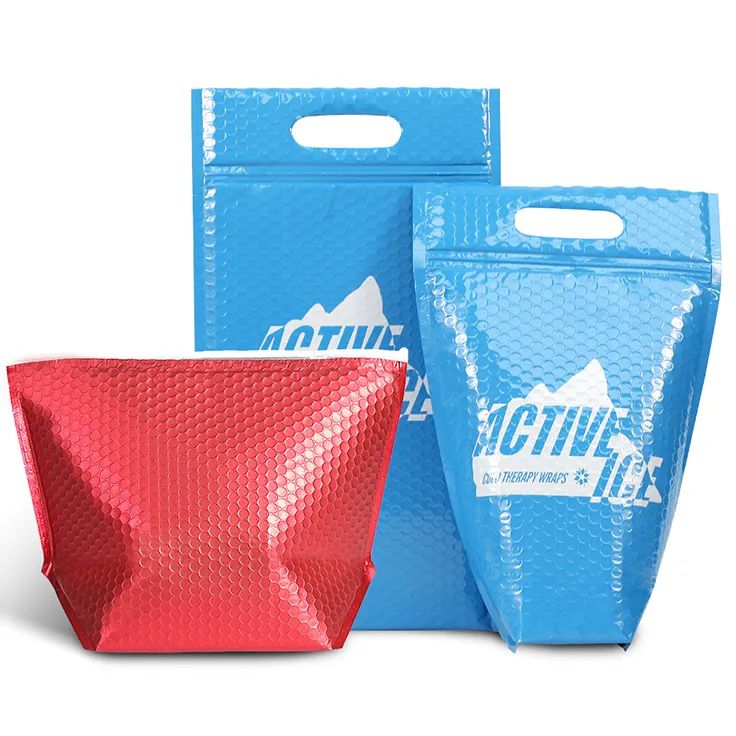
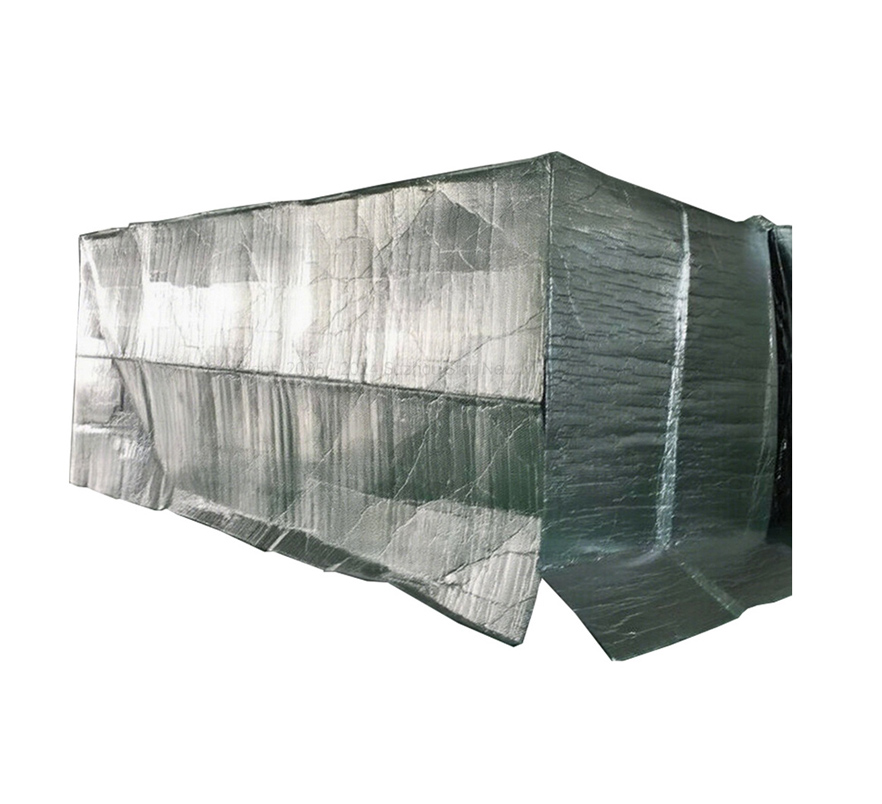
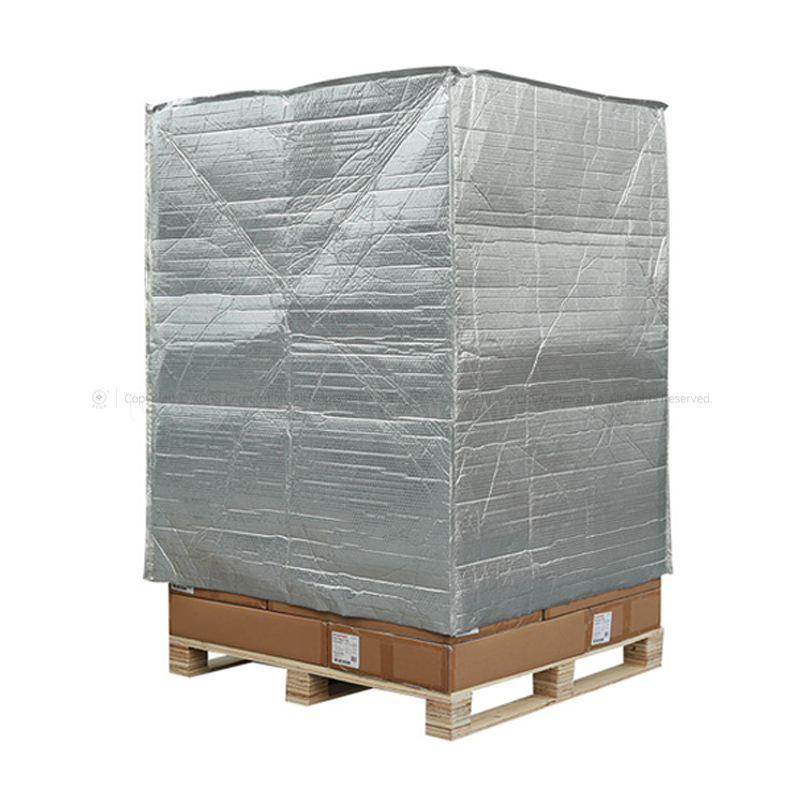
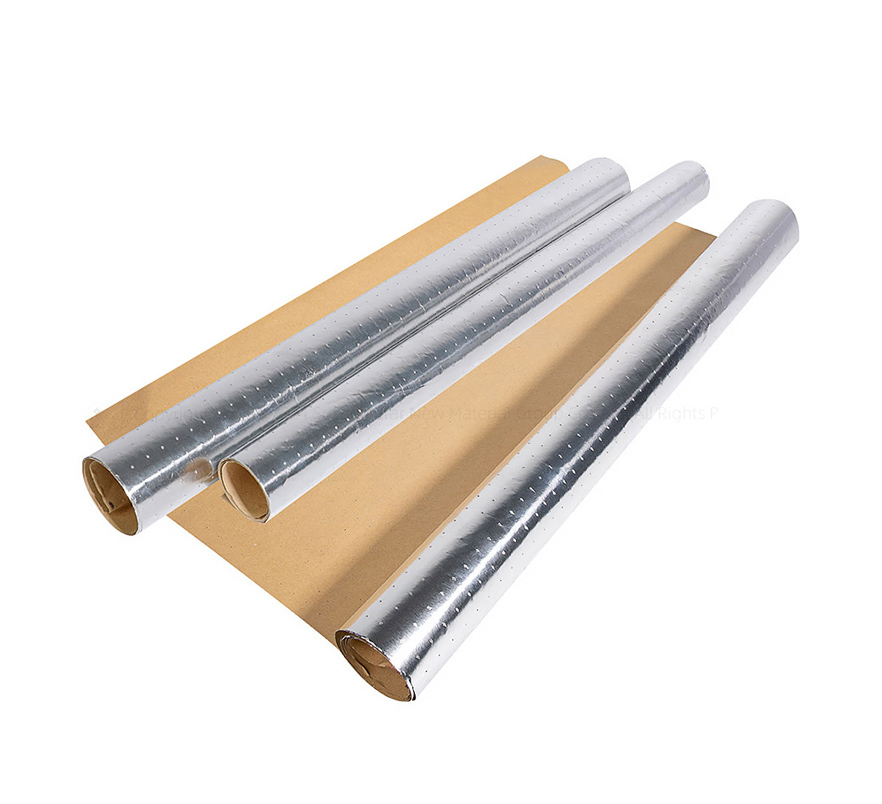
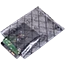
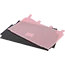
Below, I will recommend a new type of heat insulation material - XCGS Heat Insulation Material! This material is made of aluminium foil multilayer composite material on both the inner and outer surfaces, with PE polyethylene air bubble/XPE foam in the middle layer, and the thermal conductivity is only 0.032-0.036 W/m.K. It obtained the domestic invention patent in 2009, and passed the highest level test of fireproofing performance by AWTA, an authoritative agency in Australia, in 2013.


XCGS Heat Insulation adopts high-quality pure aluminium film as its outer surface layer, which has a reflectivity of up to 97%, effectively blocking most of the heat radiation. Its middle layer consists of multi-layer PE airbags, even if a small amount of heat passes through the aluminium foil to reach the middle layer, due to the existence of nano-holes, the heat can only be transferred along the walls of the holes to form heat convection, which is not easy to penetrate. Finally, the bottom again uses high-quality pure aluminium film for the second reflection blocking, so that the heat is not easy to penetrate.

By controlling thermal conductivity, using radiant heat barriers and regulating the surface structure, XCGS Thermal Insulation achieves the reduction of heat conduction, control of heat radiation and reduction of heat convection transfer, providing a strong guard for temperature protection. Not only that, it also has the advantages of moisture-proof and waterproof, non-toxic and odourless, soft and lightweight and easy to install.
With the continuous progress of science and technology and people's increasing demand for energy saving and environmental protection, the research and development and application of thermal insulation materials will usher in a broader development prospect. As a pioneer in China's environmentally friendly thermal insulation material industry, Star Group will continue to play its important role in creating a more comfortable and safe living and working environment for human beings.






































































































 18915559236
18915559236 xcbxa@xcgs.com
xcbxa@xcgs.com