Static electricity is everywhere
In daily life, you have encountered these situations: when shaking hands, your fingers will suddenly feel the fingertips pinprick like tingling while touching each other; when you get up to comb your hair in the morning, your hair will often "float" up; when you pull the door handle or open the faucet, you will be "electrocuted" and hear a "pop" sound. These are the occurrence of electrostatic phenomena in the human body.
What is static electricity?
As the name suggests, static electricity is a static state of charge or non-flowing charge, there is no closed circuit or current generation, is a macroscopic temporary stay in a place of electricity.
How is static electricity produced?
In general, an object will have two kinds of charges at the same time: positive and negative charges, their quantity are equal and cancel each other out, so the object does not show charged.
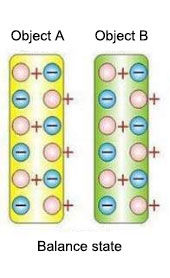
But when an object is affected by external influences (such as friction or contact with another object), the surface of the object charge will be transferred to redistribute, when the charge gathered on an object or the surface, it forms static electricity. When the positive charge gathered on an object, it forms a positive static electricity, when the negative charge gathered on an object, it forms a negative static electricity.
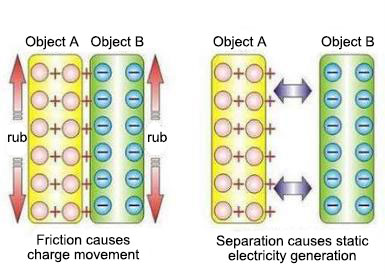
Whether positive static electricity or negative static electricity, when the electrostatic objects in contact with zero potential objects (grounded objects) or objects with a potential difference, it will occur the charge transfer, that is the spark discharge phenomenon we see every day.The charged voltage is different, the human body feels different:
Human electrically charged units | Degree of subjective feeling |
1kV | No feeling at all |
2kV | Sensation on the outside of the finger, but no pain, can hear a faint discharge sound |
2.5kV | Sensation of needle touch, shivering sensation, but no pain |
3kV | Sensation of being pricked by a needle, slight pain |
4kV | Sensation of deep pricking by a needle, slight pain in the finger, faint light of discharge visible |
5kV | Pain from the palm of the hand to the wrist, shimmering light extending from the fingertips |
6kV | Sharp pain in fingers, heavy wrist |
7kV | Sharp pain in fingers and palm, slight numbness |
8kV | Numbness from the palm of the hand to the wrist |
9kV | Severe pain in the wrist and severe numbness in the whole hand |
10kV | Pain in the whole hand and a sensation of electricity flowing through it |
11kV | Sharp numbness in the fingers and a strong feeling of electric shock in the whole hand |
12kV | The whole hand feels like it is being struck by a strong blow. |
Getting here, someone may ask: the voltage of static electricity is actually so high? Not 220 volts is already very dangerous? Then why static electricity does not cause electric shock injury to people?
This is although the electrostatic voltage is high, but the total charge is very small and it is released instantly (microsecond level). Therefore, when the human body electrostatic discharge, people just feel a slight tingle then the power has been released.
After reading these, we have a certain understanding of static electricity, if you want to know more about static electricity and how to prevent static electricity knowledge, please subscribe us now!
XCGS ESD SHIELDING PACKAGING SERIES:





































































































 18915559236
18915559236 xcbxa@xcgs.com
xcbxa@xcgs.com